USGS Groundwater Information
|
USGS Groundwater Information > April 2, 2018 Highlights USGS Monthly Groundwater News and Highlights: April 2, 2018Subscribe and get the latest USGS groundwater news and science sent to your inbox every month! Featured Product: Understanding Contamination in Fractured-Rock Aquifers![Screenshot of model simulation [ Screenshot of model simulation ]](images/feature/2018-04-01.jpg)
Figure: Bromide tracer concentration in a transport model simulation with no matrix diffusion, for time 1000 hours after the start of tracer injection. Source: Figure 8, Tiedeman and others, 2018. Improper disposal methods, leaking tanks and pipes, and chemical spills have contaminated fractured-rock aquifers in and around many industrial area across the Nation. In areas underlain by fractured rock, the management of the groundwater resource is complicated by the complex geometry of bedrock fractures, which may act as conduits and barriers to flow. USGS research in these complex environments provides the science and tools to understand the actual versus perceived health risks due to anthropogenic chemical contaminants that have persisted for decades in fractured-rock aquifers, and to provide the science needed to economically and effectively minimize exposure and actual health risks. Two recently-released USGS journal articles illustrate the critical importance of using modeling to inform design, monitoring, and expectations of bioremediation in fractured-rock aquifers in order to evaluate mobilization of chloroethene compounds from the rock matrix. Together, these articles illustrate that one cannot solely collect groundwater quality samples from permeable fractures to accurately measure the mass of the contaminant mobilized by bioremediation. One must conduct detailed site characterization in fractured aquifers, in particular, synthesizing geologic, geophysical, hydraulic, and geochemical information through groundwater flow modeling in order to accurately design remediation strategies that target specific volumes of the aquifer, and accurately forecast the success of remedial actions. USGS Groundwater-Related Press Releases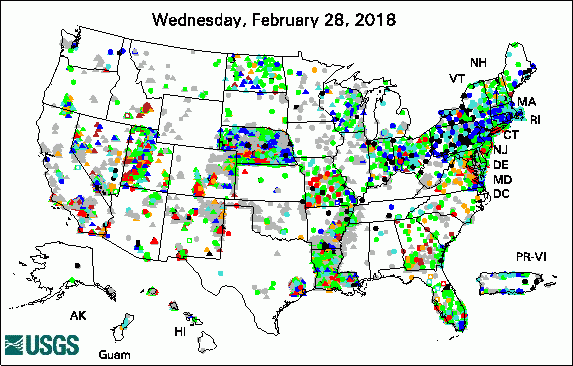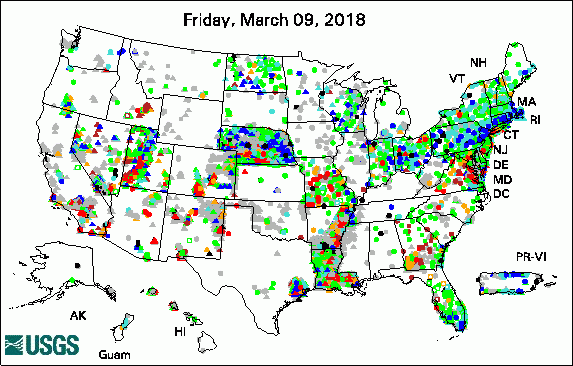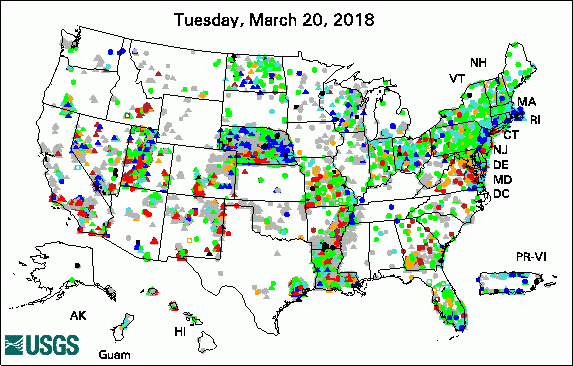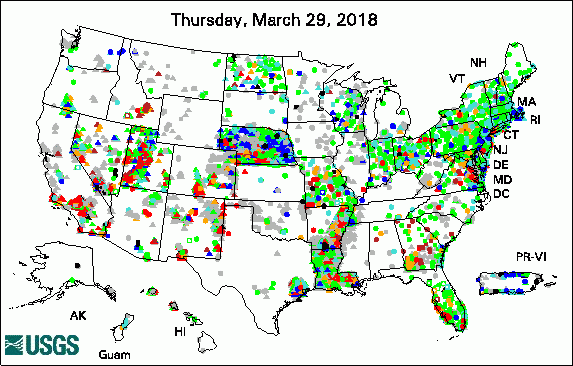 
The USGS Active Groundwater Level Network includes about 20,000 wells that have been measured by the USGS or USGS cooperators at least once within the past 13 months. The animation shows a daily snapshot of water-level statistics in the network for March 2018. Credit: USGS. The image is in the public domain. Media Advisory: Water Levels to be Measured in 1,300 Southern Idaho Wells (3/12/2018) USGS Groundwater-Related PublicationsGroundwater-level data from an earthen dam site in southern Westchester County, New York (03/26/18) Hydrologic assessment of the Edwin B. Forsythe National Wildlife Refuge (03/19/18) ModelArchiver -- A program for facilitating the creation of groundwater model archives (03/02/18) Volcanic aquifers of Hawai'i -- Hydrogeology, water budgets, and conceptual models (03/02/18)
USGS Groundwater-Related Software Updates and New Releases
Field PhotoUSGS research helps us understand how contamination moves through fractured-rock aquifers in order to inform environmental managers' decisions about how to characterize, monitor, and treat contaminated groundwater. As part of this science, USGS conducts long-term field experiments at a former aircraft engine test facility, the USGS Naval Air Warfare Center (NAWC) Research Site in West Trenton, New Jersey. High concentrations of trichloroethene persist in sedimentary rocks despite two decades of groundwater pumping and treatment at the site. In this photo, a USGS scientist prepares equipment used for a bioaugmentation experiment at the NAWC Research Site. The bladders contain solutions that were injected into the subsurface. The injection well is in front of the blue barrel. Archive of Past Highlights: |