USGS Groundwater Information
|
USGS Groundwater Information > October 1, 2015 Highlights USGS Monthly Groundwater News and Highlights: October 1, 2015Featured Product: USGS Groundwater Resources Software: Tools You Can UseDid you know that the USGS develops dozens of groundwater software applications? Building on decades of experience, the USGS continues to lead in the development and application of computer software that allows hydrologists to address scientific and management questions of increasing complexity. USGS groundwater software ranges from data visualization and graphing tools to complex groundwater flow and transport models. Most of this software is public domain, open-source code that is freely available from the USGS Water Resources Groundwater Software web site. Examples of recent major releases include: The Groundwater Toolbox, a graphical and mapping interface for analysis of hydrologic data: The Groundwater Toolbox allows for the retrieval of hydrologic time-series data (streamflow, groundwater levels, and precipitation) from the USGS National Water Information System (NWIS). The Groundwater Toolbox, which was first released earlier this year, has multiple methods for the analysis of streamflow-hydrograph data. 1DTempPro, a computer program for the analysis of one-dimensional vertical temperature profiles: This program is a graphical user interface (GUI) to the previously published USGS code VS2DH, which numerically solves the flow and heat-transport equations. The program allows users to calibrate VS2DH models against measured data to estimate vertical groundwater/surface-water exchange and also hydraulic conductivity for cases where hydraulic head is known. 1DTempPro v.2.0 was released this month and includes new features for automated parameter estimation, layer heterogeneity, and time-varying specific discharge. RRAWFLOW, a rainfall-response aquifer and watershed flow model: RRAWFLOW is a lumped-parameter model that simulates streamflow, springflow, groundwater level, solute transport, or cave drip for a measurement point in response to a system input of precipitation, recharge, or solute injection. Stay up to date on the latest USGS groundwater software updates and releases by subscribing to our RSS feed
USGS Groundwater-Related Press Releases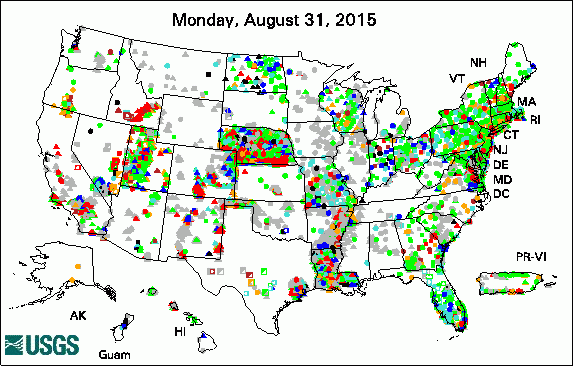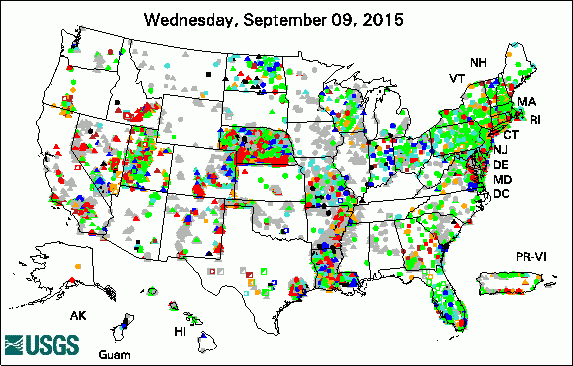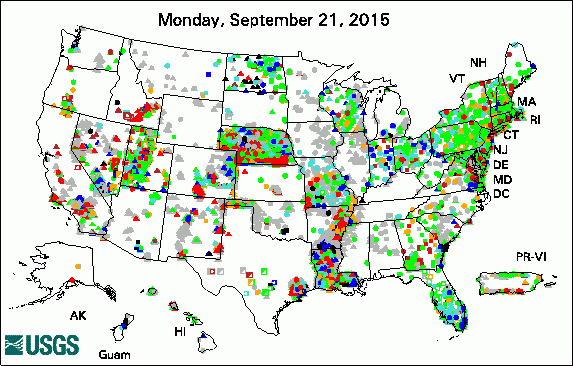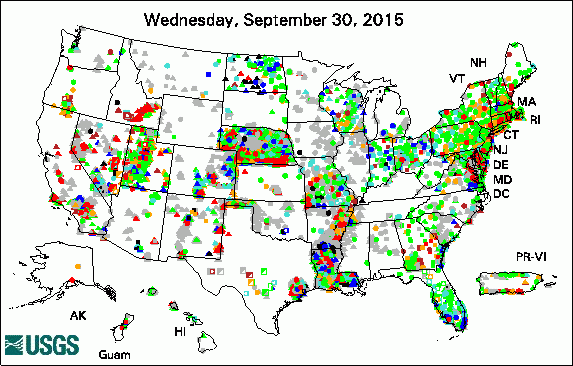 
The USGS Active Groundwater Level Network includes about 20,000 wells that have been measured by the USGS or USGS cooperators at least once within the past 13 months. The animation shows a daily snapshot of water-level statistics in the network for September 2015. Credit: USGS. The image is in the public domain. USGS Groundwater-Related PublicationsWill the effects of sea-level rise create ecological traps for Pacific Island seabirds? Comparison of evaporation at two central Florida lakes, April 2005-November 2007 Groundwater resources of the Columbia Plateau regional aquifer system Groundwater availability in the United States: the value of quantitative regional assessments Bistability of mangrove forests and competition with freshwater plants Trends in pesticide concentrations and use for major rivers of the United States 1DTempPro V2: new features for inferring groundwater/surface-water exchange Water withdrawals in Florida, 2012 Late Quaternary history of the Atacama Desert USGS Groundwater-Related Software Updates and New Releases
Field Photo:Did you know that USGS has Water Science Centers across the Nation? USGS hydrologists collect groundwater data and study groundwater conditions at sites around the United States to provide data and information policy makers and resource managers can use to inform their decisions. In this photo, a hydrologist from the USGS Indiana-Kentucky Water Science Center is preparing to conduct a 24-hour aquifer test. An aquifer test is a controlled field experiment made to determine the hydraulic properties of water-bearing and associated rocks. The test is made by observing groundwater flow that is produced by known hydraulic boundary conditions such as variations of head along a connected stream, pumping wells, changes in weight imposed on the land surface, or changes in recharge. Archive of Past Highlights |