 |
Recharge is the addition of water to the ground-water system.
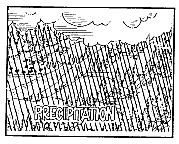
The recharge of freshwater begins as precipitation. Precipitation
occurs in several forms, including rain, snow, and hail, but only
rain is displayed on the poster. Some of the rain infiltrates
into the soil. If the rate of the rainfall exceeds the rate of
infiltration, surface water will flow over the land surface to
surface-water bodies such as rivers and streams.
|
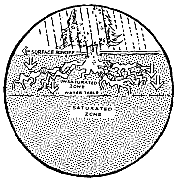 |
Water can infiltrate faster from the land surface into sandy soils
than silty or clay soils. Water infiltrates into the soil and
the unsaturated zone. The unsaturated zone occurs immediately
below the land surface and contains both water and air in the
pores and fractures in the rock materials. Water moves, or percolates,
down through the unsaturated zone to the saturated zone. The
saturated zone is where all the pores or fractures in rock materials
are filled with water. The top of the saturated zone is called
the water table.
|
 |
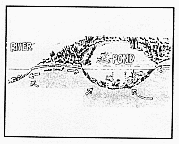
Because surface-water and ground-water systems are connected,
surface water can recharge ground water. Aquifers can obtain
water from such surface-water bodies as reservoirs and streams
when and where the water table is lower than the surface-water
body. Recharge areas usually are higher in elevation than discharge
areas.
|