USGS Groundwater Information
|
USGS Groundwater Information > May 1, 2018 Highlights USGS Monthly Groundwater News and Highlights: May 1, 2018Subscribe and get the latest USGS groundwater news and science sent to your inbox every month! Featured Product: Most atolls will be uninhabitable by the mid-21st century because of sea-level rise exacerbating wave-driven flooding![Graph of modeled chloride concentrations in drinking water over time [ Graph of modeled chloride concentrations in drinking water over time ]](images/feature/20180501_feature.png)
Figure: Graph of forecasted impact of annual wave-driven flooding events on groundwater potability at Roi-Namur Island (Kwajalein Atoll). Within 2 years of annual flooding with +0.4 meters of sea-level rise, seawater contamination causes island groundwater chloride concentrations to exceed the potability threshold. Source: Figure 4, Storlazzi and others, 2018. In a new study, scientists found that sea-level rise and wave-driven flooding on atoll islands will make their limited freshwater resources non-potable by the middle of the 21st century, directly threatening the sustainability of human populations that live there. The primary source of freshwater for populated atoll islands is rain that soaks into the ground and remains there as a layer of fresh groundwater that floats on top of denser saltwater. Scientists from the USGS, Deltares, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa used a variety of climate-change scenarios to project the impact of sea-level rise and wave-driven flooding on atoll infrastructure and freshwater availability. Based on current global greenhouse gas emission rates, the interactions between sea-level rise and wave dynamics over coral reefs will lead to an annual wave-driven overwash of most atoll islands by the mid-21st century. Such annual flooding would result in the islands becoming uninhabitable due to frequent damage to infrastructure and the inability of their freshwater resources to recover between overwash events. View the news release, or download the journal article. USGS Groundwater-Related Press Releases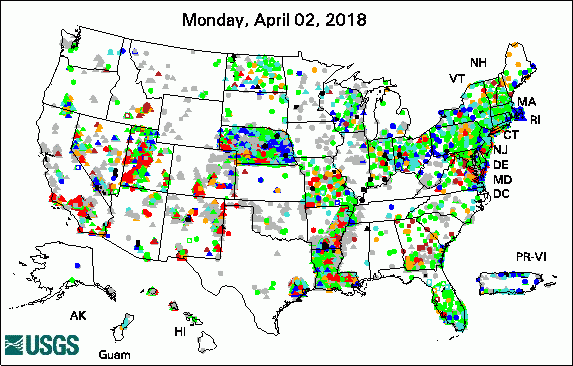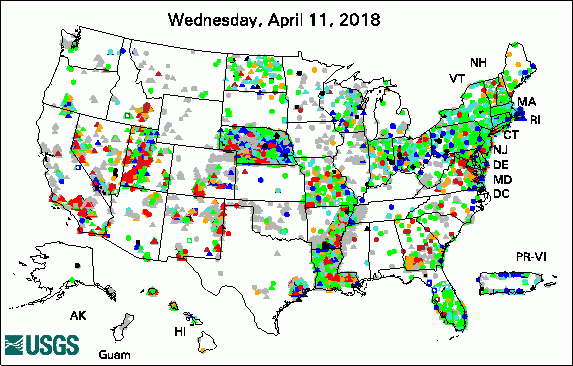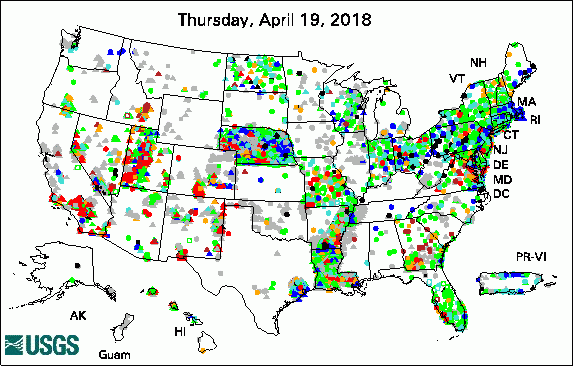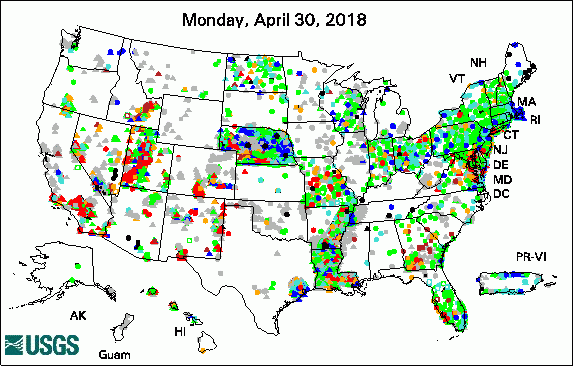 
The USGS Active Groundwater Level Network includes about 20,000 wells that have been measured by the USGS or USGS cooperators at least once within the past 13 months. The animation shows a daily snapshot of water-level statistics in the network for April 2018. Credit: USGS. The image is in the public domain. Many Low-Lying Atoll Islands Will Be Uninhabitable by Mid-21st Century (4/25/2018) New App for Lake Houston Provides Real-Time Data (4/12/2018) USGS Releases New Web-Based Groundwater Model Visualization Tool (4/12/2018) Public Invitation: The Scoop on Western South Dakota's Vital Water Resources (4/11/2018) USGS Groundwater-Related PublicationsPublic-Supply Water Use and Self-Supplied Industrial Water Use in Tennessee, 2010 (04/26/18) Carbonate system parameters of an algal-dominated reef along west Maui (04/24/18) Uranium concentrations in groundwater, northeastern Washington (04/19/18) Groundwater-level data from an earthen dam site in southern Westchester County, New York (04/18/18) Cyclic heliothermal behaviour of the shallow, hypersaline Lake Hayward, Western Australia (04/17/18) Methane in groundwater from a leaking gas well, Piceance Basin, Colorado, USA (04/10/18) Springs as hydrologic refugia in a changing climate? A remote sensing approach (04/10/18) Water resources science of the U.S. Geological Survey in New York (04/10/18)
USGS Groundwater-Related Software Updates and New Releases
Field PhotoDid you know that USGS groundwater databases include records from about 850,000 wells that have been part of USGS groundwater studies over the past 139 years? In this photo, USGS groundwater hydrologist Bill Eldridge lowers a transducer into an observation well near Jewel Cave National Monument in South Dakota to monitor groundwater-level changes in the Madison aquifer. The data will be used to update previously published groundwater-altitude maps to help better understand groundwater flow. The work is being conducted by the USGS Dakotas Water Science Center in cooperation with the National Park Service. View current groundwater conditions in wells in the USGS South Dakota Active Water Level Network. Archive of Past Highlights: |