Cape Cod Research
In This Document:
Summary
The 3H-3He method is used along with extensive sampling to determine not only average aquifer properties, but also detailed characteristics of a regional flow system and a sewage plume over a distance of four kilometers in a sand and gravel aquifer located on Otis Air Base in Falmouth, Massachusetts. 3H-3He ages increase with depth in individual piezometer clusters and with distance down flowpaths. However, the age gradient with depth (Δt/ΔDz) is smaller in the plume than that above or below the plume in the regional waters, due to the intense loading near the infiltration beds. The tritium bomb peak in precipitation is archived longitudinally along a flowline through the main axis of the plume. The tritium bomb peak in precipitation is also archived vertically in individual piezometer clusters. On the eastern side of the sampling area where water from Ashumet Pond forces plume waters deeper into the flow system, 3H-3He ages are very young at depth because the 3H-3He 'clock' is reset due to outgassing of tritiogenic 3He in the pond. A reconstruction of the tritium input functions for the regional and plume samples shows there is no offset in the peak [3H]+[3Hetrit] concentrations for the plume and regional waters which indicates that the water from supply wells for use on the base is very young. 3H-3He ages and detergent concentrations in individual wells are compared with the known time history of detergent use. The 3H-3He ages are consistent with the beginning of use of detergents and the time period when their concentrations in sewage would have been greatest. Ages, velocities, hydraulic conductivities, and recharge rates calculated using the 3H-3He data compare well with those from previous investigations and from particle-tracking simulations. The lack of agreement between 3H-3He ages and particle-tracking ages in wells downgradient from Ashumet Pond is attributed to the choice of parameters in the model used to represent the boundary or flux between the pond and the aquifer, or the properties of the aquifer downgradient of the pond.
Investigators:
Stephanie Dunkle Shapiro (LDEO, Palisades, New York), Denis LeBlanc (U.S. Geological Survey, Marlborough, Massachusetts), Peter Schlosser (Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University, Palisades, New York, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University, New York), and Andrea Ludin (Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University, Palisades, New York, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University, New York)
Publications:
Shapiro, S.D., 1998, Evaluation of the 3H-3He Dating Technique in Complex Hydrologic Environments: Ph.D. Dissertation, 254 p., Department of Earth and Environmental Science, Columbia University in the City of New York.
Shapiro, S.D., D. LeBlanc, P. Schlosser, and A. Ludin, 1999, Characterizing a Sewage Plume Using the 3H-3He Dating Technique: Ground Water, v.37, no.6, pp.861-878.
Illustrations:
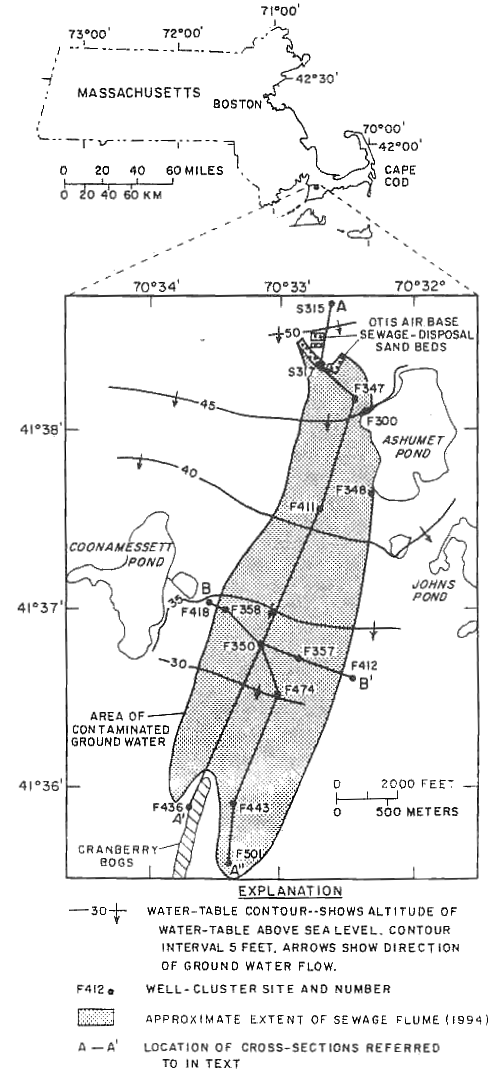
Map of study area showing sewage infiltration beds, sampling locations, Ashumet Pond, estimated extent of the sewage plume (1994), cross-sections A-A', A-A’’, and B-B', water table elevations (in feet), and general direction of ground-water flow (modified from LeBlanc, 1984).
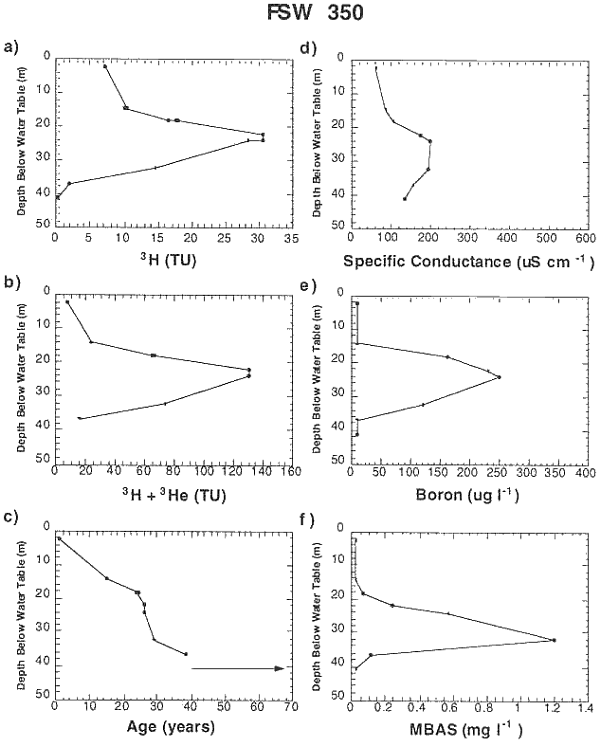
(a) [3H] (TU), (b) [3H]+[3Hetrit] (TU), (c) 3H-3He age (years), (d) specific conductance (uS cm-1), (e) boron (ug l-1), and (f) detergents (mg l-1 MBAS) versus depth below water table (meters) for cluster FSW 350. Samples with 3H-3He ages greater than 40 years are plotted with an arrow, the point of which corresponds to the age determined based on tritium concentrations alone assuming a pre-bomb input of 5 TU (see text for discussion).
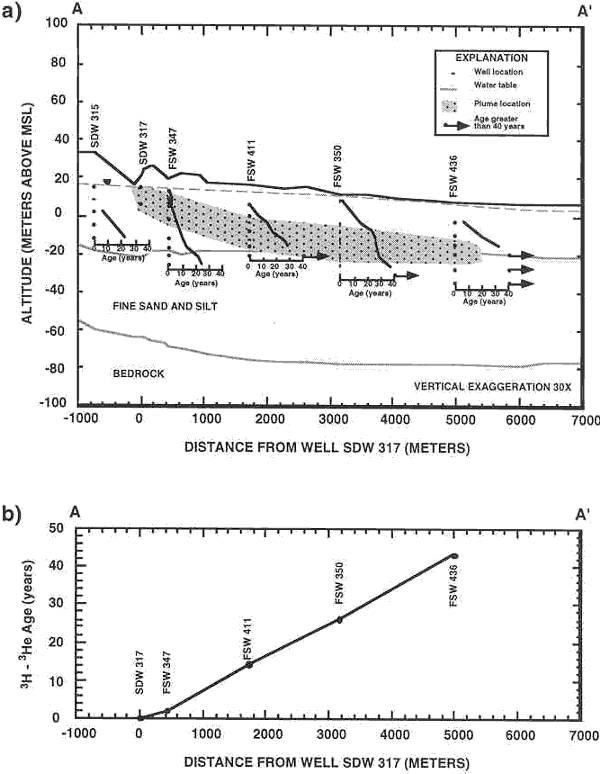
(a) Cross-section A-A’ showing 3H-3He ages in individual piezometer clusters. Also shown are the approximate location of the plume, approximate water-levels, and general lithology of the aquifer sediments. (b) 3H-3He ages in piezometers along a single flowline through the core of the plume where concentrations of boron and detergents have maximum values.
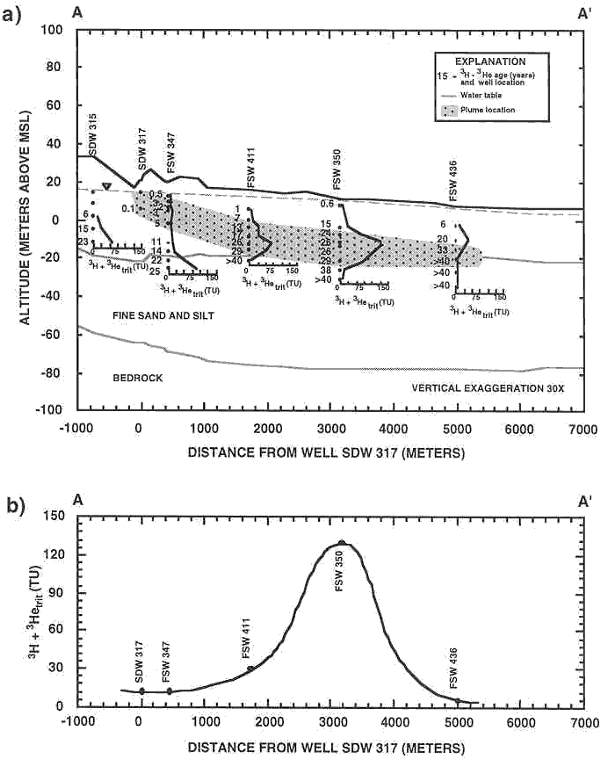
Cross-section A-A’ showing [3H]+[3Hetrit] concentrations (TU) in in individual piezometer clusters. Also shown are the 3H-3He ages, the approximate location of the plume, approximate water-levels, and general lithology of the aquifer sediments. (b) [3H]+[3Hetrit] concentrations (TU) in piezometers along a single flowline through the core of the plume where concentrations of boron and detergents have maximum values.
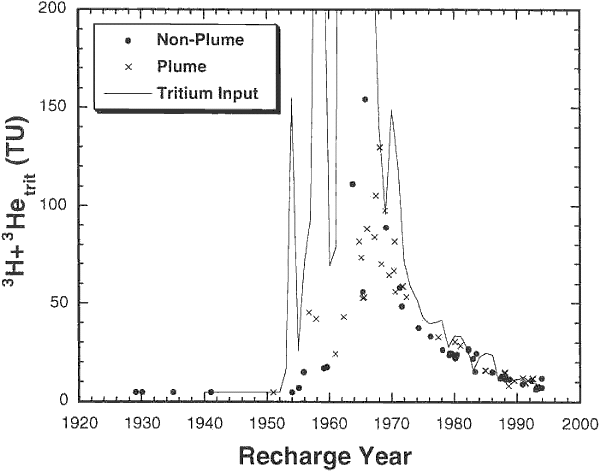
[3H]+[3Hetrit] (TU) versus 3H-3He recharge year for plume and non-plume samples. Tritium input for Boston, MA included for comparison (see text for discussion).