USGS Groundwater Information
|
USGS Groundwater Information > March 1, 2016 Highlights USGS Monthly Groundwater News and Highlights: March 1, 2016Featured Product: USGS Science is Open Science -- the USGS Public Access Plan![USGS public access plan [ USGS public access plan ]](images/feature/20160301-public-access-plan.jpg)
Learn more about the USGS public access plan. USGS has released a new public access plan outlining new measures to improve public access to USGS-funded science. The plan enables the USGS to expand its current on-line gateways to provide free public access to scholarly research and supporting data produced in full or in part with USGS funding, no matter how it is published. The public access plan supports USGS compliance with the 2013 Federal Open Data Policy. USGS has many existing repositories to provide public acccess to USGS groundwater-related science: Open DataNational Water Information System (NWIS): download groundwater-level data Water Quality Portal (WQP): download USGS water-quality data USGS Science Data Catalog: browse and search metadata records for datasets and data collections Open Source CodeUSGS Water Resources Groundwater Software: browse and download scientific software Open Access to USGS ReportsUSGS Publications Warehouse: browse and download reports by USGS scientists USGS Groundwater-Related Press Releases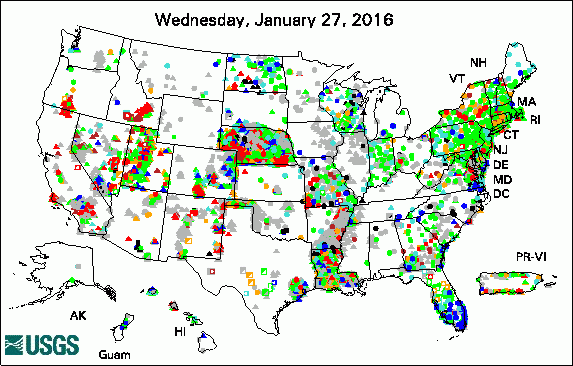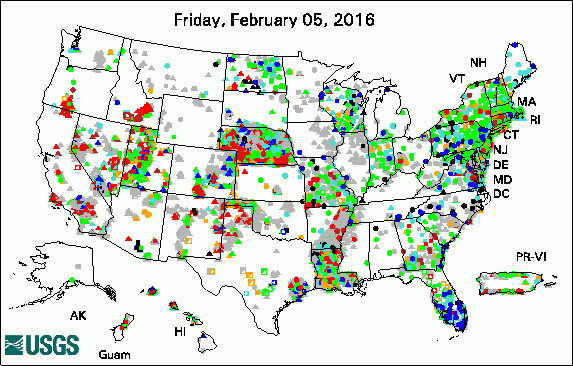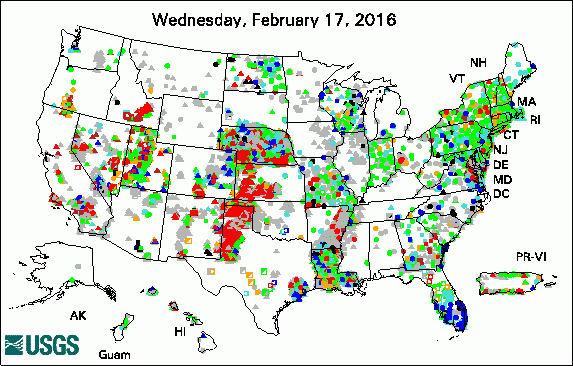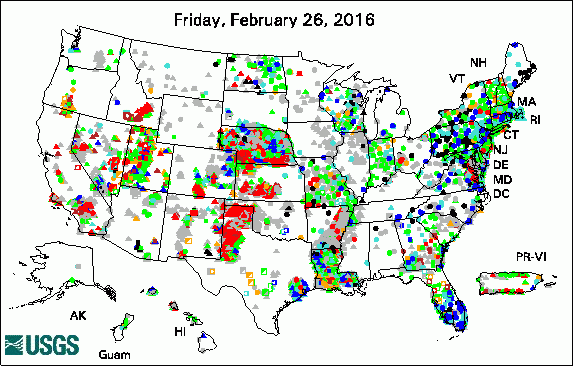 
The USGS Active Groundwater Level Network includes about 20,000 wells that have been measured by the USGS or USGS cooperators at least once within the past 13 months. The animation shows a daily snapshot of water-level statistics in the network for February 2016. Credit: USGS. The image is in the public domain. Multidisciplinary Science Addresses Complex Resource and Environmental Issues President's 2017 Budget Proposes $1.2 Billion for the USGS USGS Increases Public Access to Scientific Research
USGS Groundwater-Related PublicationsArsenic in groundwater of Licking County, Ohio, 2012 -- Occurrence and relation to hydrogeology T-COMP-A suite of programs for extracting transmissivity from MODFLOW models
Field Photo: USGS Groundwater WellWater-level measurements in observation wells are the main source of information about the hydrologic stresses acting on aquifers and how these stresses affect groundwater. Collecting groundwater levels at selected observation wells over time -- sometimes for decades or more -- is one important task conducted by the USGS to help us understand groundwater recharge, storage, and discharge in our major aquifers. In many USGS wells, USGS uses pressure transducers to automatically record the water level in a well as it changes over time. These devices, typically installed at a fixed depth in the well below the water surface, sense the change in weight/pressure of the water above it (and thus the height of the water or water level) over time. The data are remotely transmitted to a USGS office or downloaded by a scientist/hydrologic technician visiting the well. 
USGS groundwater site 414831072173002. Credit: USGS/C.B.Dawson. Photo is in the public domain. Click on photo for larger version.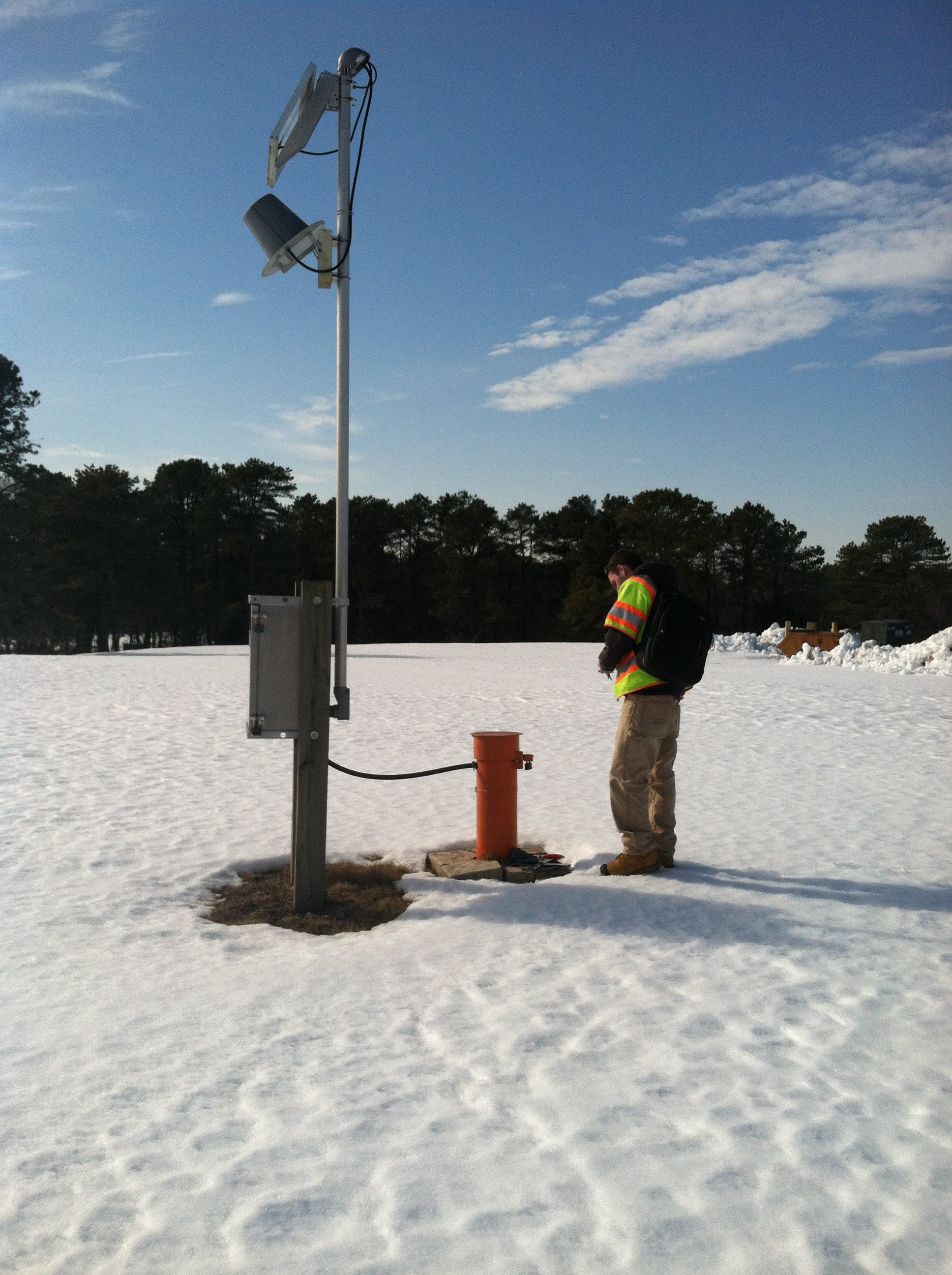 
USGS groundwater site 405149072532201. Credit: USGS/Kris McSwain. Photo is in the public domain. Click on photo for larger version. Archive of Past Highlights: |