ACTIVITY
Recharge -Discharge
Introduction
Recharge is the addition of water to an aquifer. Recharge can occur from precipitation or from surface-water bodies suc has lakes or streams. Water is lost from an aquifer through discharge. Water can be discharged from an aquifer through wells and springs, and to surface-water bodies such as rivers, ponds, and wetlands. The following activity is designed to demonstrate the recharge and discharge of water to a model aquifer.
Objectives - Students will:
- Identify several sources of recharge for ground water. Identify several sources of discharge for ground water. Discuss how water moves from recharge to discharge areas.
- Discuss the connection between surface water and ground water.
Materials
- One clear container at least 15-cm wide x 22-cm long x 6-cm deep for each group. Possible containers include clear plastic salad containers or clear baking pans. Sufficient pea-size gravel to fill the container approximately 2/3 full. Two 472-mL paper cups for each group. One pump dispenser from soft-soap or hand-lotion containers for each group. 472 mL of water. Grease pencils, one for each group. Twigs or small tree branches, to represent trees on the model (optional).
- Colored powdered-drink mix or food coloring (optional).
Teacher Preparation
- Display a copy of the poster titled "Ground Water: The Hidden Resource" on the classroom wall several days prior to conducting this activity. Using an ice pick or awl, punch 8 to 10 small holes in the bottom of one of the paper cups. When filled with water, this cup will be used to simulate rain.
- Fill the clear containers 2/3 full with pea-size gravel.
 |
Divide the class into small groups. Provide each group with one clear container filled 2/3 with pea-size gravel, one 472-mL cup with holes punched in the bottom, one 472-mL cup with no holes, and one pump dispenser. | |
 |
Students make models to represent hills and a valley. One student from each group fills the 472-mL cup without holes in the bottom with water. Each group makes a valley in the center of the model by pushing gravel to the farthest opposite ends of the container so the valley extends completely across the width of the container. About 2 cm of pea-sized gravel remains in the bottom of the valley. | 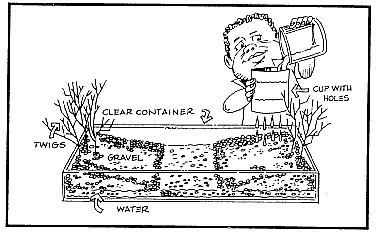 |
 |
 |
 |

