There are two things we want to estimate in the model: the hydraulic conductivity distribution and the seepage rate from the disposal pond. Initially, we assigned a uniform hydraulic conductivity of 0.0001 m/s because we only have information on bulk properties of the system, not the actual spatial distribution; this value was our best guess about the average hydraulic conductivity. In MODFLOW, there are three components of the hydraulic conductivity to assign, represented by the data sets Kx, Ky, and Kz. In this case, Kz is unimportant because there is only one layer. It is important to note that Kx, Ky, and Kz are all independent data sets, so if we only estimate Kx, Ky is unaffected. In ModelMuse, the default formula for Ky is Kx (so that the system is horizontally isotropic), so normally, you do not need to worry about keeping them synchronized with one another (if that is what you want to do). Once the MODFLOW input files are being modified by PEST, however, that will not be the case by default. The Node Property Flow (NPF) package has options to use horizontal and vertical anisotropy instead of directly specifying Ky and Kz. To use those options, select Model|MODFLOW Packages and Programs and in the NPF package, select the option to use horizontal anisotropy as illustrated below. Typically, you would also select the option to use vertical anisotropy but that will have no effect in this model because there is only one layer.
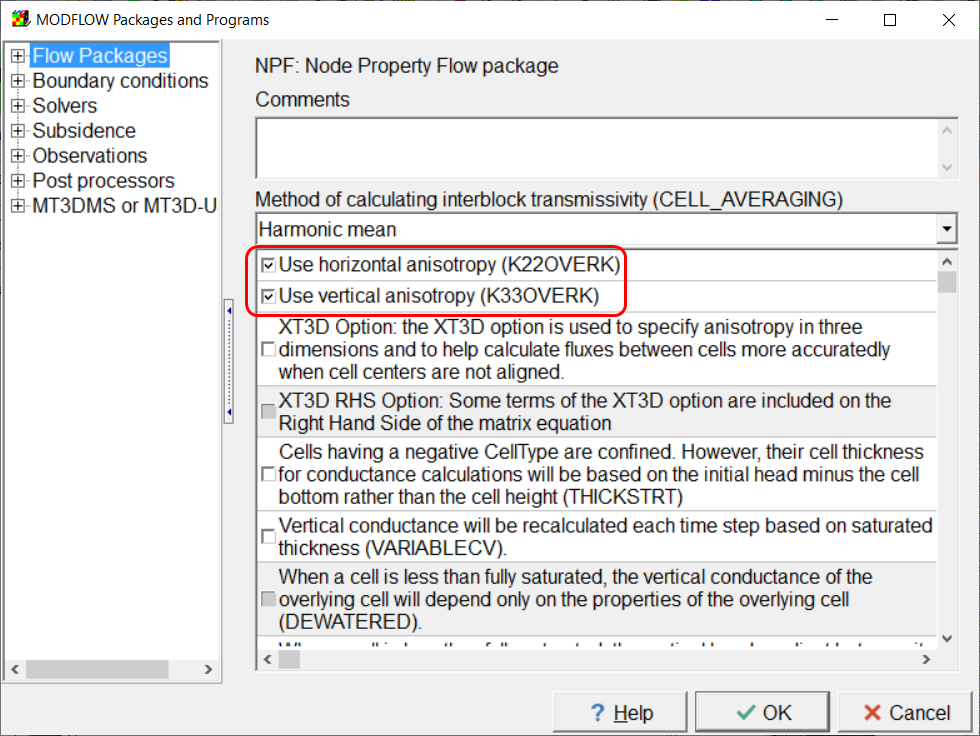
Screen capture of the MODFLOW Packages and Programs dialog box illustrating activating the options to use horizontal and vertial hydraulic conductivity by checking the "Use horizontal anisotropy (K22OVERK)" and "Use vertical anisotropy (K33OVERK)" checkboxes.