National Water-Quality Assessment (NAWQA) Project
Go to:
Over the past two decades, pesticides or their transformation products have been detected in ground waters of more than 43 states. At least 143 pesticides and 21 transformation products have been detected, including compounds in every major chemical class. For two of the multistate studies -- the National Pesticide Survey and the midcontinent investigation by Kolpin and others (1995) -- the most frequently detected pesticide compounds were transformation products, rather than parent compounds. Pesticides that have been detected more frequently (see Figure 3) include those that have been used more extensively, such as the triazine and acetanilide herbicides (atrazine, simazine, alachlor, and metolachlor), and those for which sampling has been most extensive because of contamination problems (aldicarb and its transformation products, DBCP, and ethylene dibromide, or EDB).
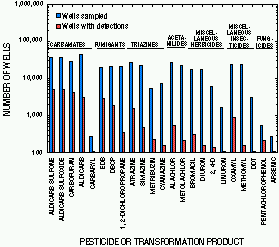
Frequencies of pesticide detection in ground water may also be substantial in non-agricultural settings. The National Pesticide Survey and the midcontinent pesticide study (Kolpin and others, 1995) included analyses of ground waters for non-agricultural pesticides. In both studies, two predominantly non-agricultural herbicides -- DCPA (in the form of one of its principal transformation products) and prometon -- were among the pesticides detected most frequently. Non-agricultural settings in which pesticides have been detected in ground water include golf courses, commercial and residential areas, rights-of-way, timber production and processing areas, and public gardens.