Water Resources of the United States
The following documentation was taken from:
U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 94-4002:
Nationwide summary of U.S. Geological Survey regional regression equations for
estimating magnitude and frequency of floods for ungaged sites, 1993
North Dakota is divided into three hydrologic regions (fig. 1). The regression equations developed for these regions are for estimating peak discharges having recurrence intervals T that range from 2 to 500 years. The explanatory basin variables used in the equations are contributing drainage area (CA), in square miles; and main channel slope (S), in feet per mile. The regression equations were developed from peak-discharge records available for 192 continuous- and partial-record streamflow gaging stations and are applicable to rural, unregulated streams draining 1,000 square miles or less. The standard errors of estimate for the regression equations range from 55 to 98 percent. The equivalent years of record range from 2.0 to 12.0 years. The report by Williams-Sether (1992) includes basin and flood-frequency characteristics of the streams used to define the peak-flow relations. The report also includes basin and flood-frequency characteristics of streams with drainage areas over 1,000 square miles and that were not used to define the peak-flow regression relations.
Topographic maps, the hydrologic regions map (fig. 1), and the following regression equations are used to estimate the needed peak discharges QT, in cubic feet per second, having selected recurrence intervals T.
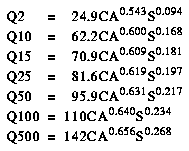
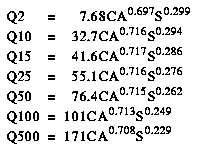
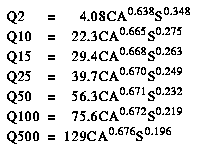
Figure 1. Flood-frequency region map for North Dakota. (PostScript file of Figure 1.)