 |
Wetland
A naturally occurring filtering system that improves water quality
by reducing nutrients while providing wildlife habitat. |
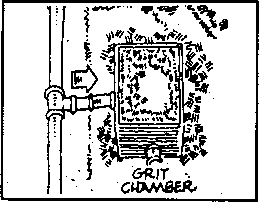 |
Grit Chamber
The initial step for raw sewage where heavy materials that might
damage equipment or interfere with later processes are removed
from raw sewage. |
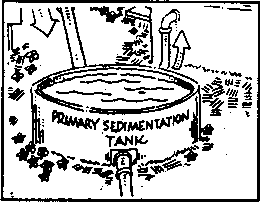 |
Sedimentation Tank
A structure designed to remove suspended solids. The speed of
flow is decreased as wastewater moves through this tank, and suspended
solids sink to the bottom and are removed. This mass of solids
is called raw sludge. |
 |
Sludge Treatment
Sludge is that part of wastewater that settles to the bottom.
Sludge is removed from the bottom of tanks and filters. Prior
to use or disposal, sludge is treated with chemicals and heat
to kill disease-causing organisms and decrease the water content. |
 |
Sludge Composting
Composting uses biological processes to generate heat to kill
disease causing organisms. By forcing air into the compost pile,
more oxygen is available to the biological organisms that decompose
the sludge. The treated sludge can be used as fertilizer, burned,
or placed in a landfill. |
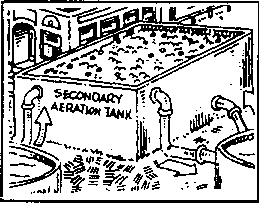 |
Activated Sludge
Wastewater is mixed with air and microorganisms in an aeration
tank, and the microorganisms break down organic matter. From
the aeration tank the wastewater is piped to another sedimentation
tank to remove remaining suspended solids. The treated wastewater
or effluent may be disinfected by chlorine before being released
to the environment. |
 |
Trickling Filter
A bed of stones from 0.9 to 1.8 meters deep through which wastewater
passes. Microorganisms, including bacteria, collect on the rocks
and consume most of the organic matter in the wastewater. The
treated wastewater or effluent may be disinfected by chlorine
before being released to the environment. |

