Water Education Poster - Navigation
Navigation Poster for Elementary School Students
sketch of its river profile. Compare the similarities and differences between the groups' river profiles.
Extension
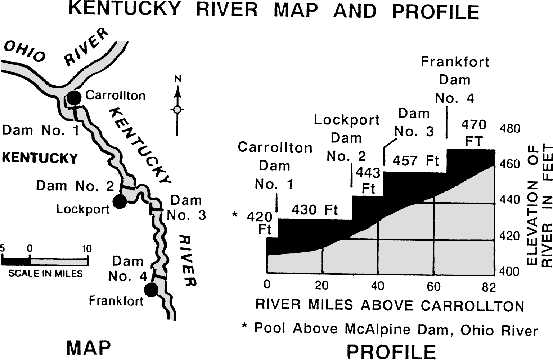
- Below is a map showing sections of the Kentucky and Ohio Rivers. The profile shows the elevations of the navigation pools along the Kentucky River south of its confluence (joining) with the Ohio. Have the students determine the difference in elevation between each pair of adjacent dams. (Answers: 1 & 2 - 13 ft.; 2 & 3 - 14 ft.; 3 & 4 - 13 ft.)
DEFINITIONS
Barge - Long, unpowered, flat-bottomed boat used to transport cargo on water; pushed or pulled by a powered boat.
Dam - Barrier built across a river to create a pool of water for navigation, flood control, water supply, or power generation.
Domestic - Within the United States.
Dredge - Machine equipped with a scooping or suction device used in deepening and widening harbors and waterways.
Harbor - Sheltered part of a water body deep enough to provide anchorage for ships or boats.
Lock - Walled navigational structure to allow raising or lowering vessels from one water level to another.
Locking through - Using a navigation lock to "step" up or down on a river.
Port - Region or city having a natural or artificial harbor with equipment, facilities, warehouses, and berths for ships taking on or discharging cargo or passengers.
Sediment - Solid material (gravel, sand, and silt) that settles to the bottom of a river.
Towboat - Powerful boat with a flat bottom and flat front used to push barges on rivers and other calm waterways.
Tugboat - Powerful boat with V-shaped bottom and rounded front used to pull barges on open water or maneuver ships in ports.
Vessel - Boat or ship intended for navigation on water.
 |
 |
 |

