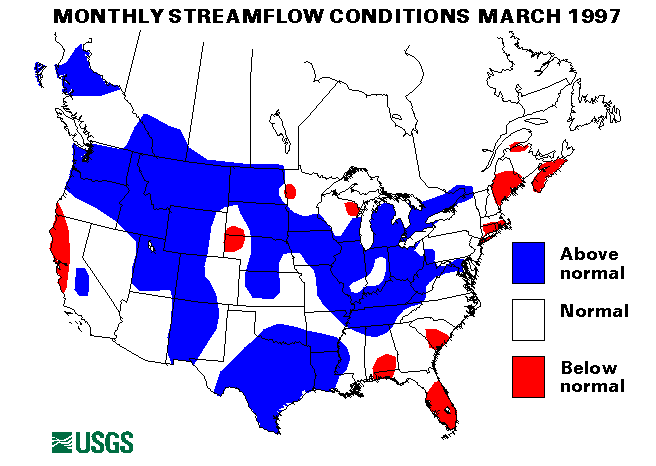
Record flooding hit several areas in Kentucky during the first week of March following extremely heavy rainfall. Louisville, Kentucky, recorded 10.48 inches of rain on March 1. Lexington, Kentucky, recorded 8.92 inches from March 1-8. Record peak flows were recorded on the Rolling Fork, Licking River, Little River, Bayou Creek and Salt River. More information on the flooding in Kentucky.
Because of the high tributary inflow, major flooding was experienced along the Ohio River from West Virginia to the confluence with the Mississippi at Cairo, Illinois, throughout the month. The recurrence interval of the flood at the Ohio River at Louisville, Kentucky, gage was estimated to be 25-years. Several deaths were attributed to this Ohio Valley Flooding. The crest at Shawneetown, Illinois, was 21.5 feet above flood stage on March 11. The crest reached Cairo, Illinois, on March 18.
New maximum March mean flows were established at the index gaging stations on the Licking River at Catawba, Kentucky, and the Green River at Munfordville, Kentucky, with 424 percent and 308 percent of the long-term (1961-90) median flows for March, respectively.
Eastern Great Lakes Region
Rainfall of 8-10 inches across southern Ohio and Indiana on March 1-2 caused extensive flooding. Flooding was severe along the Ohio River in Ohio and Indiana and along tributary streams. Record flood peaks were recorded on Ohio Brush Creek near West Union, Ohio, and Shade River near Chester, Ohio. Five people died as a result of the flooding. More information on the flooding in Ohio.
Mid-Continent South Region
From 6 to 8 inches of rain fell on the Llano River watershed in Texas on March 9 causing very rapid rises on the Llano and Devils Rivers. The Llano River was rising at a rate of a foot every 20 minutes. The flooding was moderate along the river lowlands.
Heavy rains of 2 to 3 inches across south central Texas on March 11 caused flash flooding. On March 12 over 8 inches of rain fell at Alvin, Texas. High water closed some Interstate highways in the Houston area.
Flooding along the Mississippi River near New Madrid, Missouri, crested on March 13. This broad flood peak affected areas from Missouri to Louisiana throughout the month as much of the river was over flood stage. On March 26 the crest was at Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Victoria, Texas, received 4.49 inches of rainfall on March 16-17 which boosted their March total to a record 10.89 inches. Lowland flash flooding resulted from this heavy rainfall.
New maximum March mean monthly flows were established at index gaging stations at Saline Bayou near Lucky, Louisiana, and the North Bosque River near Clifton, Texas, with flows of 253 percent and 1899 percent of median.
Western Great Lakes Region
Flooding continued along rivers in Illinois through March 27. The Illinois, Embarrass, Wabash, and Rock Rivers were especially affected. The Illinois River was as high as 10 feet above flood stage at some locations.
Snowmelt flooding started about March 21 in Minnesota when warmer temperatures moved into the area. Flooding was reported along the Minnesota, Redwood, and Cottonwood Rivers in southern Minnesota. More information on the flooding in Minnesota.
Southeast Atlantic Region
Up to 6.5 inches of rain were reported in western North Carolina on March 13 causing some flash flooding problems.
On March 29, heavy downpours over much of northwest Georgia caused mud slides and flash flooding.
Northwest Region
Extremely heavy rain on the south slope of the Olympic range in Washington caused record peak flows on the Wynoochee, Satsop, and Skokomish Rivers. Rainfall at Wynoochee Dam totaled 22.36 inches (including 10.96 inches in 24 hours) over the period March 16-19.
Heavy rains on March 19-20 over the Cascades in Washington caused flooding on the Skokomish, Snoqualmie, Snohomish, Skagit, and Yakima Rivers.
Mid-Continent North Region
Significant runoff from rapid snowmelt caused many streams and rivers to rise to or above flood stage in Iowa, North Dakota, and South Dakota, beginning about March 21. In Iowa, the basins affected were the Little Sioux, Cedar, Iowa, and Des Moines rivers. The Cannonball, Knife, Heart, Little Missouri, Souris, and missouri Rivers and Apple Creek were affected in North Dakota and the James, Vermillion, Big Sioux, and Rock Rivers in South Dakota. More information on the flooding in North Dakota and South Dakota
Intermountain West Region
Snowmelt and ice jams caused flooding in Montana beginning about March 21. The Yellowstone and Milk Rivers were especially affected. Moderate flooding was reported in low lying areas along these rivers. The Yellowstone River at Corwin Springs, Montana, index station established a new maximum March mean flow of 1370 cubic feet per second cubic feet per second (ft3/s), 146 percent of long-term median.
New York and New England Region
Mild temperatures, rainfall, and snowmelt pushed streams over their banks in Vermont and northern New York on March 30. Flooding was only minor.
Alaska
All four streamflow index stations in Alaska had flows in the normal range.
Hawaii
One of the three reporting streamflow index stations in Hawaii had above-normal flows. The East Branch of North Fork Wailua River near Lihue, Kauai, Hawaii, was 152 percent of the long-term median for March. The other two sites had normal flows.
Puerto Rico
Both streamflow index stations in Puerto Rico had flows in the normal range.
Big Three Rivers
The combined flows of the three largest rivers in the lower 48 states-- the St. Lawrence, the Mississippi, and the Columbia--increased 49 percent from last month to 1,948,000 cubic feet per second (ft3/s). This flow was 59 percent above median and above normal. The St. Lawrence River at Cornwall, Ontario, near Massena, New York, set a new maximum March mean monthly flow of 324,000 cubic feet per second (ft3/s), 126 percent of March median. The Mississippi river at Vicksburg, Mississippi, rose 66 percent from February and was at 167 percent of median. The Columbia River at The Dalles, Oregon, increased 32 percent from last month and was 177 percent of median.